Table of Contents
Clinical Validation of SaMD: What You Need to Know

Overview
Clinical validation of Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) ensures a software’s safety and effectiveness for its intended medical use. It involves rigorous testing and evidence collection to demonstrate that the software performs as claimed, provides reliable results, and meets the regulatory standards for patient care.
Short Summary
- Clinical validation is an integral part of clinical evaluation of an SaMD, which is defined as a set of ongoing activities conducted for the assessment and analysis of an SaMD’s clinical safety, effectiveness and performance as intended by the manufacturer.
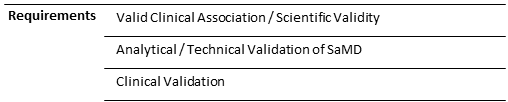
- Key requirements of clinical evaluation of SaMD include valid clinical association, analytical or technical validation of SaMD, and clinical validation.
- Clinical validation is essential to ensure an SaMD works as intended.
SaMD and SaMD Categorization
Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) refers to software that is intended to be used for medical purposes but is not part of a hardware medical device.
The SaMD definition, as outlined in SaMD N12, is utilized by the SaMD manufacturer to clarify the intended medical use of the SaMD (such as treating, diagnosing, managing, or informing clinical decisions). It also specifies the healthcare context or condition the SaMD addresses (whether critical, serious, or non-serious) and details its core functionality.2
The manufacturer uses these elements from the SaMD definition statement to classify the SaMD within the categorization framework depicted in the chart. 2
| State of Healthcare | Significance of information provided by SaMD | ||
| Treat or Diagnose | Drive Clinical Management | Inform Clinical Management | |
| Critical | IV | III | II |
| Serious | III | II | I |
| Non-Serious | II | I | I |
Once an SaMD is categorized based on its intended use and healthcare context, the next critical step is to evaluate its clinical performance, ensuring it meets the necessary safety and effectiveness standards.
What Is Clinical Evaluation of SaMD
The clinical evaluation of SaMD involves a series of continuous activities to assess and analyse the device’s clinical safety, effectiveness, and performance according to intended use. Clinical validation (a key component of clinical evaluation) verifies that the software performs its intended functions reliably, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and building trust among users.
Clinical evaluation and validation are essential for ensuring that the SaMD is safe, effective, and suitable for its intended use. They also play a key role in gaining regulatory approval and building trust among healthcare providers and patients.2
Requirements of Clinical Evaluation of SaMD
Clinical evaluation of SaMD is crucial to ensure that the software meets safety and effectiveness standards before it reaches the market.
The main requirements for the clinical evaluation of Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) are:
Valid Clinical Association/Scientific Validity
Valid clinical association, also called scientific validity, refers to how well the results from an SaMD–such as its concepts, conclusions, or measurements–are accepted or supported by established scientific evidence. It also depicts how accurately these results reflect the real-world healthcare situation and condition defined by the SaMD.2
Analytical/Technical Validation of SaMD
Analytical validation checks if an SaMD produces accurate and reliable results based on input data. In simpler terms: 2
- It ensures the software processes input data correctly and consistently and produce precise output.
- It confirms the software meets its specifications and that these specifications align with user needs and its intended use.
Manufacturers usually perform analytical / technical validation during the software development phase using a quality management system (QMS).2

Fig. 1: Role of Analytical Validation
Clinical Validation
Clinical validation assesses how well an SaMD produces results that are clinically useful for its intended purpose. This means checking whether the SaMD has a positive effect on individual or public health and whether it performs its intended functions (like diagnosing, treating, predicting risk, or predicting treatment response) effectively.2
The manufacturer must evaluate clinical validity both before the SaMD is released (pre-market) and after it is in use (post-market).2

Fig. 2: Clinical Evaluation SaMD
Clinical validation involves comparing the SaMD’s performance with clinical conditions of interest and is a key component of evaluating any SaMD. It can be demonstrated by:2
- Using existing data from studies with the same intended use,
- Using data from studies with a different intended use, if justified, or
- Generating new clinical data for the specific intended use.
Conclusion
The clinical evaluation of SaMD is a critical process that ensures these digital tools are both safe and effective for their intended use. By rigorously assessing the clinical performance, accuracy, and reliability of SaMD, stakeholders can provide confidence to users and regulators alike.
The key requirements of clinical evaluation of SaMD include valid clinical association, analytical or technical validation of SaMD, and clinical validation.
As technology continues to evolve, maintaining a high standard for clinical validation will be essential to harnessing the full potential of SaMD while safeguarding patient health and advancing medical innovation.
CliniExperts provides expert guidance, streamlines regulatory processes, and offers tailored solutions to ensure compliance with industry standards, helping clients navigate the complexities of healthcare regulations while optimizing their operational efficiency and enhancing patient safety.
Their experience helps avoid pitfalls, accelerate development, and connect you with industry professionals, increasing the likelihood of successful market entry for your SaMD.
References
- Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) [Internet]. FDA. 2020.
Available from: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/digital-health-center-excellence/software-medical-device-samd
- Software as a Medical Device (SAMD): Clinical Evaluation Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff Food and Drug Administration Center for Devices and Radiological Health [Internet]. 2017.
Available from: https://www.fda.gov/media/100714/download
Recent Posts
Reduced Approval Timelines and Enhanced Compliance Obligations under NDCT Amendment Rules 2026

The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, through G.S.R. 46(E) dated 20 January 2026, has implemented critical amendments to the New Drugs and Clinical Trials (NDCT) Rules, 2019. A major aspect of th..
Introduction of “Permission or Prior Intimation” Mechanism for Test Licenses under NDCT Rules, 2026

The NDCT Rules 2026 test license framework introduces a structured permission or prior intimation mechanism, streamlining regulatory oversight for investigational products, APIs, and clinical trial ma..
India-EU Free Trade Agreement (FTA): A Strategic Boost for India’s Pharma, Healthcare, and Food Sectors

The India-EU Free Trade Agreement (FTA) is a comprehensive trade framework aimed at liberalising bilateral trade and strengthening economic ties between India and the European Union. It enhances marke..
Need Help?
Submit your EnquiryOffice Locations
India
- Delhi
- Bangalore
Global
- USA
- Singapore
Call us on
Sales: +91 7672005050
Reception: +91-11-45214546
Timings
9 am to 6 pm (Monday to Friday)