Table of Contents
Quality Management Systems for SaMD: Best Practices and Standards

Overview
Quality Management Systems for SaMD requires compliance with regulatory standards, implementation of robust quality management systems, and risk management through design controls, testing, and post-market surveillance. It also involves maintaining thorough documentation, ensuring staff competency, and incorporating cybersecurity measures to ensure software safety and effectiveness.
Short Summary
- Software as a Medical Device faces many challenges related to quality management systems.
- The 3 key principles of Software as a Medical Device Quality Management Systems include: leadership and organisational support, Software as a Medical Device lifecycle support processes, and Software as a Medical Device realisation and use processes.
- These 3 QMS principles are closely tied to the way an organisation operates.
What Is SaMD?
Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) is an emerging and rapidly expanding segment of the medical device sector. The International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) defines SaMD as software intended for medical purposes, such as diagnosis or treatment.
It is regulated based on its intended use and risk level, following guidelines like the FDA in the U.S. and EU MDR in Europe. Ongoing monitoring ensures safety and effectiveness.
The software industry uses engineering processes and excellent software quality to regulate the quality of software products. With the patient safety viewpoint taken into consideration, these procedures may easily conform to the fundamental guidelines of the quality management systems (QMS) criteria for medical devices.2
Key QMS principles for SaMD manufacturers
An effective QMS for SaMD should incorporate the following key principles:
- Leadership and Organisational Support: An organisational structure that provides leadership, accountability, and governance with adequate resources to assure the safety, effectiveness, and performance of SaMD.
- SaMD Lifecycle Support Processes: Implementation of scalable and consistent processes throughout the SaMD lifecycle that adapt to the organisation’s size and maintain quality.
- SaMD Realization and Use Processes: Development of scalable processes for SaMD realization and use, focusing on essential elements that guarantee safety, effectiveness, and performance.
The three principles should not be treated as isolated procedures within an organization. Instead, a successful QMS seamlessly integrates them as follows:

Fig. 1: Quality Management System Principles for SaMD Manufacturers
- The leadership and organization support principle should be structured such that it creates a solid base for the processes that support the lifecycle of SaMD (SaMD lifecycle and support processes).
- These life cycle support processes need to be used throughout the entire development and usage of the SaMD (SaMD realisation and use processes).
A robust governing structure is foundational for successfully managing the lifecycle of SaMD. By ensuring that lifecycle support processes are consistently applied, organizations can enhance the quality, safety, and effectiveness of their medical software products, ultimately benefiting both users and stakeholders.
SaMD Leadership and Organisational Support
The organization’s management leads all activities related to the lifecycle of SaMD, including setting strategic direction and defining roles to ensure its safety and effectiveness.
The organization’s leaders are in charge of putting the QMS into action. This involves creating a quality policy, setting quality goals, and developing project plans that focus on the customer. The governance structure of the organisation should support the creation and maintenance of the processes needed to meet these quality goals and policies.
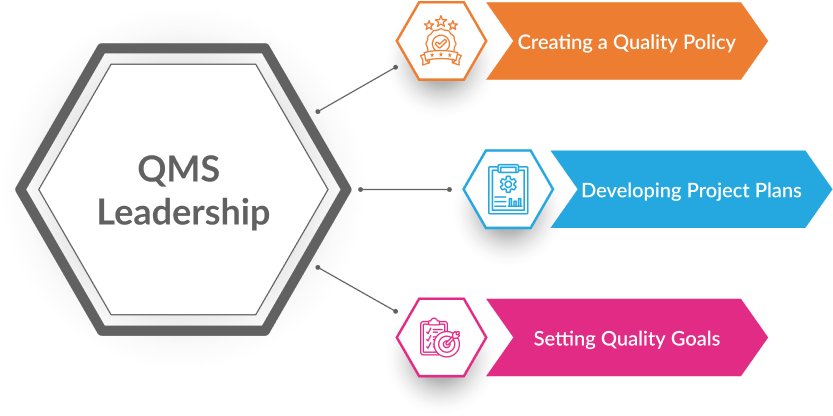
Fig. 2: Roles of leaders in the QMS
SaMD Lifecycle Support Processes
An organisation’s QMS should prioritize processes that support the SaMD lifecycle. Various methods, such as product planning, patient safety–focused risk management, document and record control, configuration management, and process improvement are used to manage these lifecycle processes. These methods are typically tailored to the complexity and size of the SaMD product and project, whether for a new product launch or an upgrade.
SaMD Realization and Use Processes
This outlines the essential lifecycle processes for methodologies used by organizations that develop SaMD. Key points to consider are:
- SaMD lifecycle support processes should be applied throughout the SaMD development and usage.
- Software engineering practices that are crucial for an effective SaMD QMS should be focused on.
- The activities in this process should be seamlessly integrated into the chosen development methodology/approach, instead of being executed in a specific order or as separate phases.
Conclusion
As the IMDRF states, the three QMS concepts are not distinct activities. This implies that everything is interconnected, from management’s top choices to how individual operations are performed.
A paper-based QMS makes it difficult to see how quality management processes and data are connected. In legacy systems, users must rely on their intuition or patterns to mentally piece together the entire QMS, which makes understanding the system much harder.
However, CliniExperts provides a connected, organized, and traceable QMS ecosystem that promotes a quality-focused culture. Our platform reduces risks and the complexity and burden of quality system visibility, helping startups achieve FDA and ISO compliance.
With CliniExperts, your team can launch products faster and more efficiently while enhancing productivity and operational performance. Contact us today to strengthen your SaMD with evidence-based decision-making.
References
- Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) [Internet]. FDA. 2020.
Available from: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/digital-health-center-excellence/software-medical-device-samd
- Software as a Medical Device (SaMD): Application of Quality Management System [Internet]. 2015.
Available from: https://www.imdrf.org/sites/default/files/docs/imdrf/final/technical/imdrf-tech-151002-samd-qms.pdf
Recent Posts
Standards, Accreditation and Validity of FSSAI-Recognised Food Testing Laboratories

Short Description FSSAI strengthens food safety in India by accrediting laboratories through NABL, enforcing Good Laboratory Practices, addressing operational challenges, and promoting global st..
Organic Food Labelling In India| Certification, and Import of Organic Food in India

This Article is All About Organic Food Labelling In India and Certification, and Import of Organic Food in India. Explained in Detail About What is Organic Food labelling? Summary Short Description Wi..
Cosmetic Label Compliance India : A Guide to Compliance

Introduction Looking for Cosmetic Label Compliance India? Are you a cosmetic manufacturer or importer navigating the complex world of Indian regulations? Ensuring your product labels comply with the l..
HAVE A QUERY?
REACH US!Office
New Delhi
Unit No. 324 & 325, City Centre Mall, Plot No. 5, Sector 12, Dwarka, India - 110075
+917672005050
Bengaluru
RMZ Galleria, 1st floor, Ambedkar Colony, Yelahanka, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India – 560064
Call us on
Sales: +91 7672005050
Reception: +91-11-45214546
Timings
9 am to 6 pm (Monday to Friday)